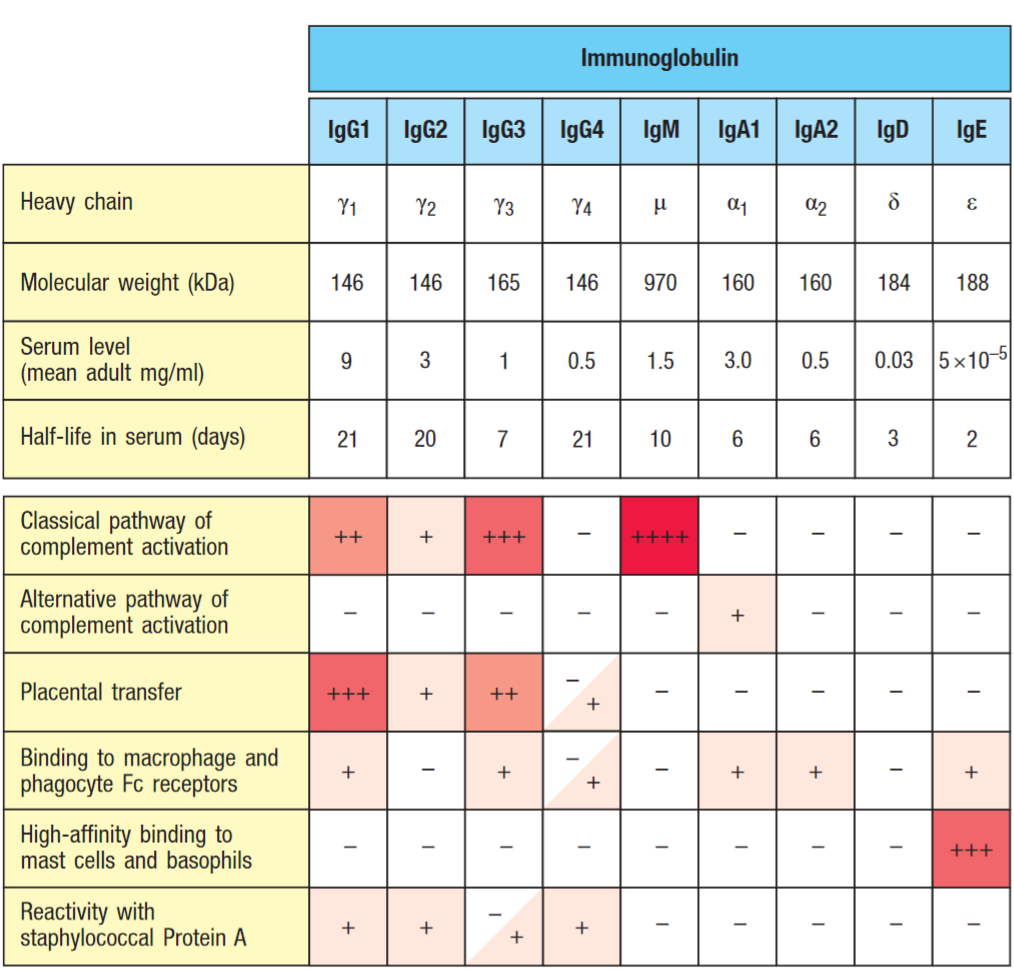
IgA antibodies
Most abundant antibody in the body and cleans up mucosa. Abundant in respiratory tract, primary sexual organs, digestive tract, mouth and respiratory tract. Neutralises pathogens at the bodies ‘doorstep’ to try prevent any infection before it starts. They are the only antibodies that can freely pass to the outer mucosa.
Can be secreted as a monomer or a dimer:
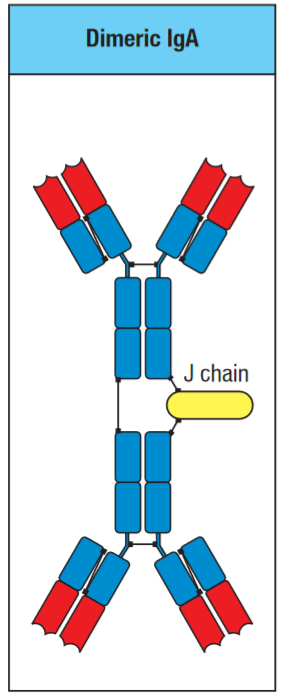
With merged Fc regions they cannot activate other immune systems such as complement or the innate immune system at all. If they could activate complement and the likes, constant inflammation would occur in the gut, mouth and respiratory tracts.
The conjoined Fc regions make IgA antibodies very effective at clumping pathogens together to be swallowed in snot or expelled in feces.